Mycosis of the feet (dermatophytosis) is an infectious disease caused by pathogenic or opportunistic fungi. With mycosis, the skin on the legs peels off and is very itchy, and in severe cases, it becomes red and swollen.
Definition of disease
Mycosis of the feet, or dermatophytosis, is an infectious disease caused by dermatophyte molds. In total, 43 species of dermatophytes are known, 30 of which lead to mycosis of the feet. Most often these are the mushrooms Trichophyton rubrum (90%), Trichophyton mentagrophytes and less commonly Epidermophyton. Mycosis of the feet is caused much less frequently by fungi of the Candida genus and by the molds Scytalidium dimidiatum, Scytalidium hyalinum.
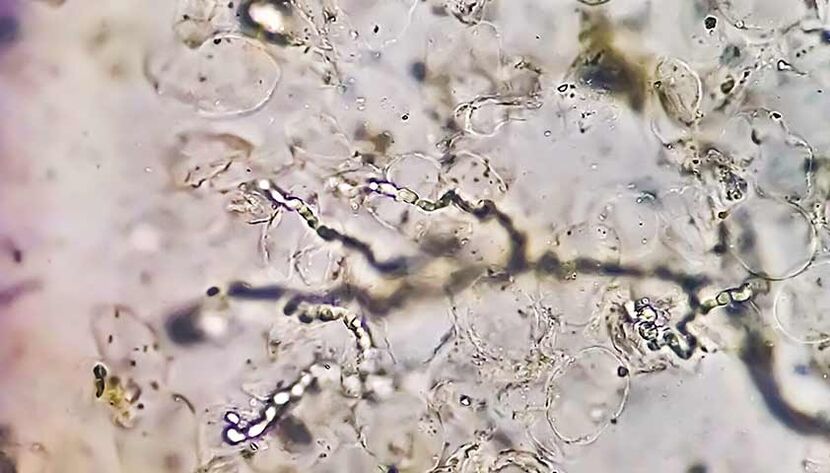
All dermatophytes have keratinolytic activity: they are able to dissolve keratin, the fibrous protein that forms the upper part of the skin of humans and animals. The skin is damaged.
Once on the skin, the fungi head to the most vulnerable places: the junctions between the cells of the epidermis. There they penetrate inside and begin to grow actively. However, fungi rarely penetrate deeper than the granular layer of the skin. They are usually limited only to the upper and keratinized tissues.
Prevalence of foot mycosis
Skin mycoses, including foot mycosis, are found in all countries of the world. The share of these diseases in the structure of all dermatological diseases reaches 37-40%.
At the same time, mycoses of the skin occur more often - in about 30% of cases.
According to dermatologists, up to 20% of the adult population suffers from foot mycosis. The pathology is found twice as often in men.
Among people over 70 years old, foot fungi are found in almost every second patient: this is explained by the fact that older people usually have chronic diseases associated with metabolic disorders, as well as vascular pathologies, such as varicose veins .
Mycosis infection of the feet usually runs in families, through direct contact with the skin of an infected person. There are also known cases of infection when sharing clothes, shoes and household items.
The infection usually affects both feet at the same time and partially spreads to the nails. Without treatment, the disease can also affect the skin of the palm, usually of the working hand. This condition is called two-feet-one-hand syndrome.
Causes of foot mycosis
Most often, mycosis of the feet is caused by dermatophyte fungi: Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Epidermophyton floccosum. Much less often, the disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida (Candida) and molds (Scytalidium dimidiatum, Scytalidium hyalinum).
According to some studies, the percentage of dermatophytes in the structure of the causative agents of mycosis of the feet gradually decreases. Candida fungi come to the fore.
Risk factors for developing foot mycosis:
- violation of personal hygiene;
- sharing shoes (for example in bowling alleys, skate and ski rental shops);
- visit public baths, swimming pools, beaches;
- climatic characteristics: the risk of getting sick is greater in countries with subtropical and tropical climates - this is due to increased humidity and ambient temperature;
- constantly wearing closed, tight shoes (this happens among military personnel, miners, workers in the textile and metallurgical industries);
- frequent toe injuries due to flat feet, calluses, calluses;
- failure to comply with health regulations during pedicure;
- impaired blood supply to the legs;
- immunodeficiency conditions, including HIV;
- chronic dermatoses;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- taking certain medications (systemic glucocorticosteroids).
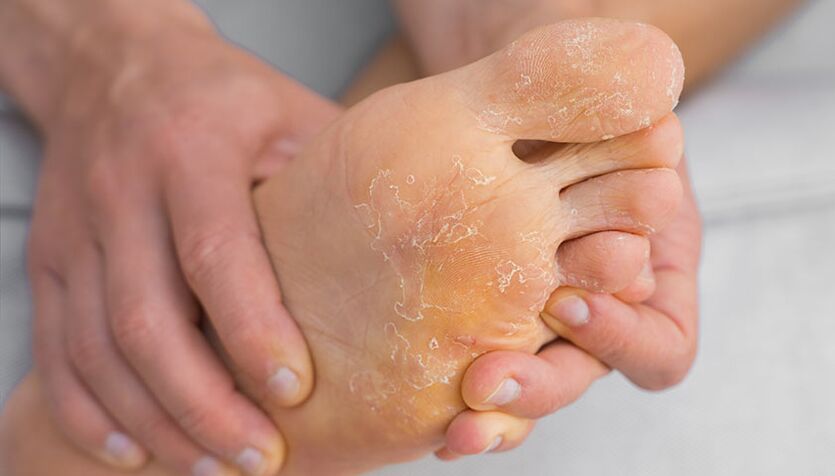
Symptoms of foot mycosis
Symptoms of mycosis of the feet and features of treatment of the disease depend on its clinical form.
Squamous (squamo-hyperkeratotic) form of mycosis of the feet
In most cases, the causative agent of the scaly form of mycosis of the feet is the dermatophyte Trichophyton rubrum.
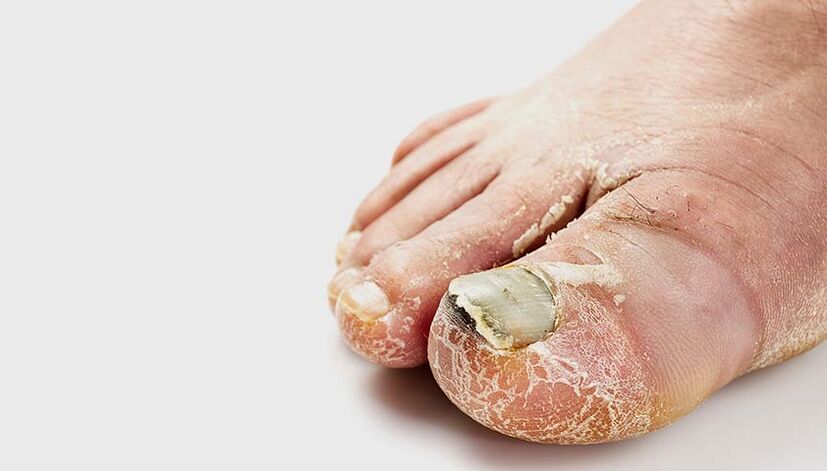
In the initial stage of the disease, the patient is bothered by moderate peeling of the skin between the fingers: the scales on the skin are abundant, thin and silvery in color. Then, as the disease spreads to the lateral and dorsal surfaces of the feet, a characteristic inflammatory ridge appears and the skin in the affected areas thickens. Over time, the patient develops onychomycosis - nail fungus.
Intertriginous (interdigital) form of mycosis of the feet
This form often develops against the background of heavy sweating of the feet. The disease affects the spaces between the toes and is accompanied by redness, swelling and maceration (softening and sagging of the skin). Erosions and cracks often form. Many patients report itching, burning and pain.
Often, a simultaneous infection of the skin of the feet with dermatophyte fungi (usually Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale) and the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus occurs.
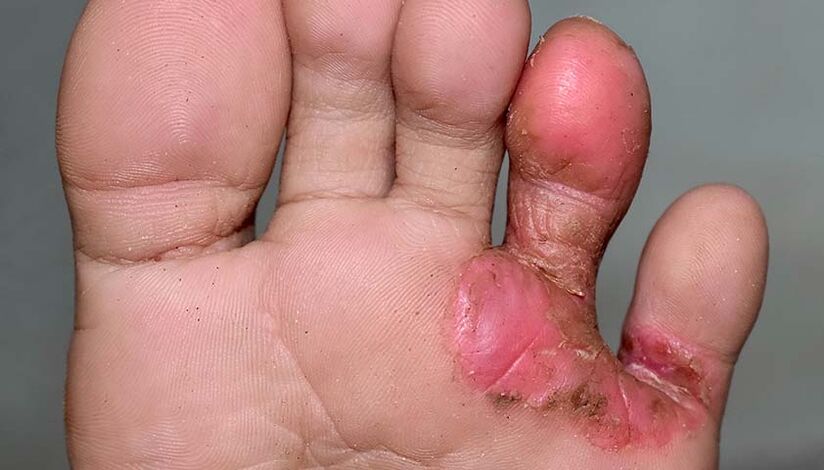
Dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet
As a rule, the causative agent of this form of mycosis of the feet is Epidermophyton floccosum (flaky epidermophyton).
The dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet, as a rule, is more severe and is accompanied by painful itching and pain. Blisters with a thick covering on the skin. Combining, they form large multichambered vesicles, which, after opening, turn into moist pink-red erosions, and then into brown crusts.
The disease is difficult to treat and often recurs.
A characteristic feature of the dyshidrotic form is damage to the arch of the foot, interdigital folds and the skin of the toes. The process can then spread to the heels, lower lateral surfaces of the feet, and even to the skin under the ankles.
If a bacterial infection occurs, the patient may develop fever and the regional lymph nodes will become enlarged. Swelling of the foot appears and the skin on it becomes wet. Severe pain makes it difficult for the patient to walk.
Exudative-dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet
Most often, the exudative-dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet is caused by the fungus Trichophyton rubrum (red trichophyton).
The skin between the toes is affected first. Then the process extends to the sole of the foot, the dorsal and lateral surfaces and the nails. Blisters and erosions appear on the skin, which then become covered with crusts. The skin gets wet and can rot.
Erased form of mycosis of the feet
The deleted form is identified by some researchers. It is believed to occur a few days after infection by the fungus.
The skin in the interdigital folds begins to peel. You may also experience light flaking on the soles and sides of your feet. Patients may ignore unpleasant symptoms, but still infect others.
Acute form of mycosis of the feet
The acute form of mycosis of the feet is the result of an exacerbation of the dyshidrotic or intertriginous (interdigital) form.
The disease begins acutely: numerous blisters appear on the skin of the feet and then on the legs. The skin swells. Then nodules form on the hands and lower third of the forearms.
After the blisters open, erosions appear surrounded by fragments of loose skin. They merge, turning into extensive weeping surfaces, often with purulent discharge.
The disease is often accompanied by fever, deterioration of the patient's general condition and acute pain in the affected hands and feet. The inguinal and femoral lymph nodes become enlarged and painful.
Vesiculobullous (inflammatory) form of mycosis of the feet
The inflammatory form of mycosis of the feet is usually identified by foreign authors, often defining it as acute. It can develop from a chronic interdigital form of dermatophytosis.
As a rule, the causative agent of the vesiculobullous form is the dermatophyte Trichophyton rubrum.
Main symptoms: severe itching, skin rashes, localized mainly on the soles of the feet, at the base and sides of the toes, on the back of the foot. Swollen areas with blisters on the surface may appear. Bubbles may merge or remain unchanged for a long time, if the tire (top) is thick enough.
Often nails are also involved in the process: onychomycosis develops.
Ulcerative form of mycosis of the feet
The ulcerative form (in foreign literature it is called deep) is one of the complications of mycosis of the feet, caused by the addition of a bacterial infection.
Extensive deep purulent ulcers form on the soles of the feet. The patient feels severe pain and, as a result, difficulty walking.
Complications of mycosis of the feet
Cracks and ulcers on the skin that appear at the site of mycosis are the gateways to bacterial infections. However, it is more difficult to treat such infections: this is explained by the fact that fungi produce special substances that increase the resistance of bacteria to drugs.
The most common complications of foot mycosis:
- allergic dermatitis of infectious and pharmacological origin;
- pyoderma - pustular skin diseases (cellulitis, lymphangitis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis of the foot bones), which can lead to deep and long-lasting skin wounds;
- plantar warts;
- microbial eczema is a chronic inflammatory disease in which the skin itches and turns red, and liquid blisters form on it;
- a general decrease in immunity and impaired microcirculation in the lower extremities (usually develops in patients with diabetes mellitus and varicose veins);
- spread of the disease on the skin of the hands and nails;
- worsening of the quality of life: in acute forms of mycosis it is difficult to wear shoes, and lymphadenitis leads to fever and poor health.

Diagnosis of mycosis of the feet
A dermatologist-mycologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of mycosis of the feet.
At the appointment, the doctor will evaluate the condition of the patient's nails, skin, mucous membranes and hair. He will conduct a dermoscopy: he will examine the skin under magnification. In parallel with the examination, the specialist will collect the medical history and ask the patient about his lifestyle, quality of nutrition, household habits and treatment procedures.
If you suspect athlete's foot, your doctor will order laboratory tests.
Examination of skin scrapings will rule out or confirm a fungal infection.
The doctor may also refer the patient for a microscopic examination and culture.
Sowing, or the cultural method, allows you to obtain more accurate information about the causative agent of the disease, although it takes more time, usually a month.
Diabetes mellitus can significantly worsen the course of mycosis of the feet and lead to serious complications. Complex studies can exclude or confirm this diagnosis.
A complete blood count helps evaluate the patient's general condition.
A clinical blood test is a blood test that allows you to evaluate the general state of health, identify inflammation, bacterial, viral and fungal infections, and can also help in the diagnosis of anemia, diseases of the blood-forming organs, allergic reactions and autoimmune diseases.
Also, before recommending antifungal therapy, the doctor may prescribe the patient a biochemical blood test: this study will determine the level of bilirubin and liver enzymes ALT and AST. Such information will help the doctor choose the dosage of the drug and minimize the risk of side effects.
Treatment of mycosis of the feet
Treatment of mycosis of the feet is carried out in two stages.
In the first phaseIn case of acute inflammation, lotions are used: aqueous solutions of ammonium bituminous sulfonate, agents with antiseptic properties (Castellani liquid, 1% aqueous solution of brilliant green). Then pastes and ointments that contain antifungal drugs and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed.
In case of severe crying (in the acute phase) and the addition of a secondary infection, anti-inflammatory solutions such as lotions are used, as well as combined antibacterial drugs in the form of creams and solutions.
The basis of therapy is the use of antifungal - antifungal agents.
On the main stagetreatment uses antifungal drugs designed to destroy pathogenic fungi. Most often such drugs are produced in the form of ointments, creams or solutions.
If the patient is bothered by severe itching, the dermatologist may prescribe antihistamines. Usually they are taken for 10-15 days, until the unpleasant symptom completely disappears.
When the nails are damaged, antifungal agents are used: they are applied directly to the nail plate and nail folds. In this case the drug concentrates on the surface of the nail and does not penetrate the bloodstream, eliminating the risk of side effects.
If external drugs do not produce an effect, systemic antifungal agents are prescribed.
The treatment regimen and dosage of drugs are determined by the doctor. During treatment you need to visit a podiatrist at least once a month.
Prognosis and prevention
If you timely consult a doctor, the prognosis for mycosis of the feet is favorable: most patients treated with antifungal drugs get rid of the disease forever.
To prevent mycosis it is necessary to protect the feet and hands from irritating and traumatic factors and strengthen the immune system.
Measures to prevent onychomycosis:
- change your socks every day or more often if your feet are sweaty or wet;
- air or dry shoes after wearing them;
- use an anti-fungal UV shoe dryer;
- do not wear shared slippers during the visit;
- do not try on shoes in a store with bare feet;
- use a personal towel for your feet;
- use individual nail care tools (tweezers, files);
- wear shoes in the pool or sauna;
- monitor the diversity of your diet;
- avoid stressful situations.
FAQ
How to cure foot fungus?
To treat fungi on the legs, antifungal drugs are usually used, which are available in the form of creams, ointments and solutions. A dermatologist should choose the most effective drug and determine its dosage.
Why do my feet itch?
One of the causes of itchy feet is foot mycosis, an infectious disease caused by dermatophyte molds.